How well can you speak and understand French? By taking the French proficiency test, you can know your accurate level of fluency and competence.
Taking an exam can help you know your strengths and pinpoint areas where you can improve. This enables you to customize your French language learning experience.
But with such a wide range of choices, which French language test should you opt for?
DELF, DALF, Telc, TEF, TCF, or a variant of DFP? The tests have many variations depending on the purpose.
We are all aware of the countless advantages of learning a language. Why should you study French when there are so many great options? The question to ask is, why not?
French is among the most widely spoken foreign languages globally, with over 30 Francophone countries.
French is an international language in various fields. This includes, but is not limited to, fashion, cuisine, wine, aeronautics, dance, visual arts, architecture, commerce, and theater, and the list is infinite!
It is highly valued and beneficial in the business world.
Learning French can open up various possibilities, including French-speaking jobs, higher studies, and immigration to France and Canada.
It can unlock new prospects and limitless potential, regardless of your goal.
And if you are learning French, you should know where you stand and get an authentic certification.
Why, How, When, Where, and Which official exam should you choose between DILF, DELF, DALF, TELC, TCF Canada, TEF, or TEF Québec?
We’ll find out about everything in this extensive guide.
Table of Contents
What is a French proficiency test?
The French proficiency tests measure an individual’s ability in the French language. They check one’s language skills in practical situations.
These tests evaluate various language skills, including listening, reading, speaking, and writing. The French exams are international ones that assess non-native French command.
Various organizations conduct these tests globally. It follows the CEFR (Common European Framework of Reference for Language) guidelines.
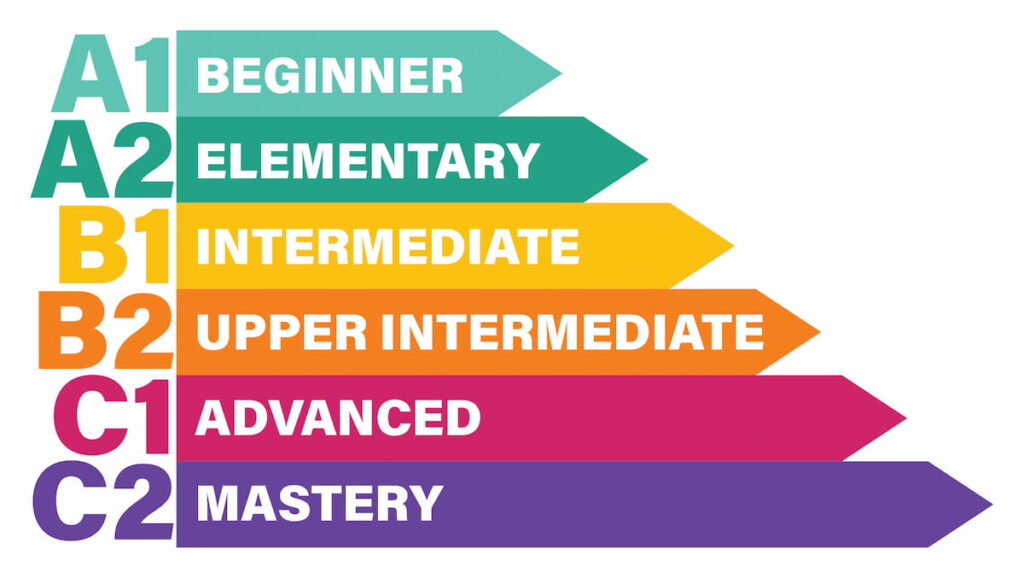
It is widely used for various pursuits, such as immigration, admissions for higher studies, employment, and personal language assessment.
Why should you take official French Exams?
Do you know French, or have you already achieved a certain level of proficiency in this language? If so, you can prove your ability by taking a French test.
Which French exam to take depends on many factors and purposes.
For example, do you want to study abroad in France, Canada, or one of the Francophone countries?
These diplomas confirm the French language skills required for admission to various universities. Most educational institutions accept them for both undergraduate and postgraduate courses.
Although not mandatory, colleges often favor international students with official French certifications.
The demand for jobs that require French is growing.
It can prove your competency when applying for jobs at companies that require knowledge of the French language.
Adding French test diplomas to your resume is a good idea because they are recognized worldwide. Guesswork is no longer part of companies’ practices. Instead, they check the official certifications stating your proficiency.
Certifications such as DELF B2 or DALF C1 and C2 can enhance career prospects, especially in roles that require advanced language proficiency.
Specific exams like TCF and TEF are recognized for individuals seeking to immigrate to French-speaking countries. They may be required as part of the immigration process.
If you’ve been studying French for a while, you might be curious about your precise skill level.
You can take the French proficiency test to evaluate your knowledge and prepare for the next test.
They are structured across different levels, providing a clear path for learners to progress from beginner levels (e.g., A1) to advanced (e.g., C2). This allows individuals to set achievable language learning goals.
Individuals can learn their shortcomings and help them study and improve their French to take their language skills to the next level. This can also increase confidence.
Since these French exams are globally approved, you do not have to worry whether they will be accepted. They provide a standard measure of language proficiency.
Top French Language Certifications in 2025

Individuals can get several types of certifications to prove their French language proficiency.
They are widely recognized and can be beneficial for various goals. This includes academic admissions, careers, and immigration. The French language tests are available for all levels – beginners, intermediates, and advanced.
A certificate or diploma selection depends on your personal or professional goals. But all are internationally recognized.
These are the diplomas and French proficiency tests that are widely recognized. Here are some of the most common certifications.
1. DILF (Diplôme Initial de Langue Française)
The French Ministry of Education offers the certification of DILF, or Diplôme Initial de Langue Française.
The DILF is the beginner-level diploma in the series of French proficiency certifications. It precedes DELF and DALF. This is specifically for those just beginning to learn French and adhere to level A1.1 of the CEFRL.
The test evaluates the candidate’s knowledge in four core areas: reading, writing, speaking, and listening.
It’s important to note that the minimum age for taking the exam is 16 years old. You can only take this French exam within French territory.

Key Features of DILF
- The DILF is for individuals learning French who want an official certification for their primary language proficiency.
- The DILF is the most basic level among the French proficiency certifications. It assesses language proficiency at the A1.1 level of CEFR.
- The test has four sections: Compréhension Orale (Listening), Compréhension Écrite (Reading), Production Orale (Speaking), and Production Écrite (Writing).
- The minimum age is 16 years.
- You can only appear for a test in France.
- After passing DILF, you may continue your French learning journey and progress to higher levels by taking subsequent exams like DELF and DALF.
2. DELF and DALF
DELF (Diplôme d’Études en Langue Française) and DALF (Diplôme Approfondi de Langue Française) are a series of official French language proficiency certifications.
These two tests are the most prestigious for non-native speakers wanting to show knowledge of French.
The French Ministry of Education awards these diplomas in association with the Centre International d’études pédagogiques (CIEP). These two assess language skills at various levels, from beginner to advanced.
Over 300,000 students enroll yearly to take the DELF/DALF exams in over a thousand testing centers worldwide.
Levels of DELF and DALF
There are six levels of DELF and DALF.
- DELF A1: Breakthrough or beginner
- DELF A2: Waystage or elementary
- DELF B1: Threshold or intermediate
- DELF B2: Vantage or upper-intermediate
- DALF C1: Effective Operational Proficiency or Advanced
- DALF C2: Mastery or proficiency (Near-native)
DELF and DALF comprise 6 independent diplomas corresponding to the CEFRL levels. You can register for the examination of your choice, as per your current level.
How to Pass DELF or DALF?
The exam assesses four skills at every level: listening, speaking, writing, and reading.
Each section has 25 marks. Thus, to earn a diploma, you must score at least 5/25 in each module and an overall score of 50 out of 100.
Where should you take the DELF/DALF test?
As of January 2025, Alliance Française and its partner network administer the DELF and DALF tests in over 1,200 exam centers in over 175 countries.
The Alliance Française network manages these exams in many cities and AF branches in India.
This includes Ahmedabad, Bengaluru, Bhopal, Bhubaneswar, Chandigarh, Chennai, Dehradun, New Delhi, Hyderabad, Jaipur, Kolkata, Lucknow, Mumbai, Panjim, Pune, Pondicherry, Udaipur, and Trivandrum.
DELF/DALF Validity
DELF and DALF certifications are valid for life and never expire. So, there’s no need to retake the test to prove your fluency later.
Different Types of DELF Exams
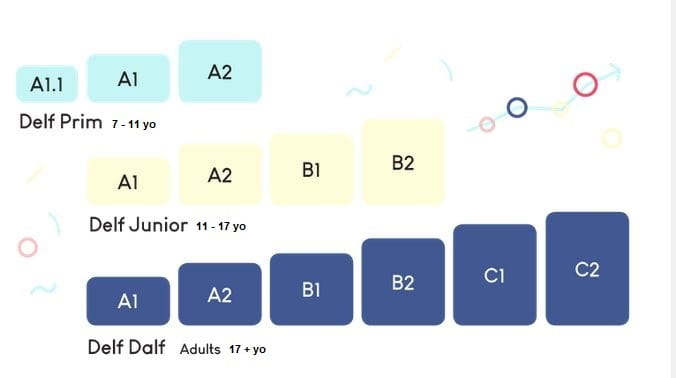
There are six different tests within the broad DELF category.
(i) DELF Prim (ages 7-11)

The DELF Prim exams are available for younger students. These tests are designated for children between 7 and 11 years old.
There are only three test levels: A11.1, A1, and A2. These tests measure beginners’ French language skills.
The exam topics are tailored to the interests of the test’s age group. They include personal details, family, friends, and everyday situations.
(ii) DELF Junior (ages 11 to 17)
The Scolaire or Junior has two types — DELF “Scolaire” and DELF “Junior.”
The DELF junior version is ideal for teenagers between 11 and 17.
The junior’s version motivates young people to learn French. This exam is mainly for learners in secondary and higher secondary schools.
There are four levels: A1, A2, B1, and B2 (beginner to independent users). The adolescent candidates can check their understanding of French in real-life and academic contexts.
DELF Junior is a specially adapted version for juniors and teenagers of the DELF diplomas.
The test structure is like the DELF for adults. Yet, the topics focus more on school-going students aged 11 and above.
The levels assess A1 to B2.
(iii) DELF Scolaire
DELF Scolaire is also for non-native French-speaking adolescents, similar to DELF junior.
Just like all variations of DELF and DALF, it has global recognition and lifelong validity.
What is the difference between DELF Scolaire and Junior?
Both are the same. The administration is the only distinct thing.
If there is an agreement between the French embassy and local schools, take the DELF for schools (DELF Scolaire).
If there is no mutual understanding, opt for DELF Junior.
(iv) DELF Pro
The target audience is professionals and adults in a work context. DELF Pro has four levels: A1, A2, B1, and B2.
These exams aim to gauge individuals’ proficiency in using French professionally. They are for learners interested in joining the French-speaking world.
France Education International has discontinued DELF Pro, so taking this exam is no longer possible. Instead, consider selecting Tout Public (A1 to B2), which is similar.
(v) DELF (Diplôme d’Études en Langue Française)
Anyone over 17 who loves French can take the DELF. The four DELF diplomas align with a CEFR scale of A1 to B2.
There are four sections in the DELF test: oral comprehension, writing, speaking, and reading comprehension.
The candidates can pick the level they perceive most suitable for their skill level.
The diploma is identical for DELF Junior and DELF Tout Public. The word “Junior” does not appear on the certificate. As a result, it is impossible to differentiate the two diplomas.
(vi) DALF (Diplôme Approfondi de Langue Française)
The DALF C1 and C2 levels show advanced or proficient skills. DALF C2, the highest French diploma for foreign language, aligns with the highest level (C2) of the CEFR.
The only variation between DELF and DALF lies in their levels.
The DELF targets A1 to B2, while the DALF is designed for C1 to C2, the highest French proficiency levels.
3. TEF (Test d’Evaluation de Français)
The TEF, or Test d’évaluation de Français, is a regulated French test. The purpose is to measure the French language ability of those who are not native speakers.
In 1998, the French Language Centre of the CCI Paris Ile-de-France established the TEF test. This has been recognized by the French Ministry of Education, Interior, Higher Education, Research, and Innovation.

Many governments also accept TEF for various purposes, such as work permits and immigration to France and Canada.
E.g., the Canadian Department of Immigration, Refugees, Citizenship, the Quebec Ministry of Immigration, Francisation, and Integration, and the Swiss State Secretariat for Migration.
Unlike DELF and DALF, TEF is a single-level test where you get a score based on your French proficiency. It checks four abilities: reading, listening, speaking, and writing. All TEF varieties are valid for only two years.
TEF provides four distinct versions that cater to various needs.
- TEF Other Purposes for study or work in France and Canada.
- TEF IRN for French nationality and Residency Card.
- TEF Canada for immigration to Canada.
- TEF for Québec Immigration.
Let’s explore the individual examination.
(i) Test d’Evaluation de Français (TEF Other Purposes)
TEF for Other Purposes is for international students who wish to pursue higher studies abroad in France and Canada. It is valuable for work, job hiring, training, and internships.
It confirms your level of French proficiency and determines your eligibility for these programs.
The grading scale has 7 levels, ranging from 0 (basic) to 6 (advanced fluency). It connects to the CEFR levels (A1 to C2) and the 12 levels of the Canadian Language Benchmarks.
Within 5 to 6 weeks after the test, they send the certificate by email. There is no limit to the number of times you can take the test. However, a one-month waiting period is necessary between two consecutive exams.
There are 5 modular tests in the TEF Other Purposes. This includes oral expression, listening comprehension, reading comprehension, vocabulary & structures, and written expression.
You can select any or all of the 5 exams based on your goals and needs. Keep in mind that you must finish this exam all at once.
(ii) TEF IRN (Intégration, Résidence, & Nationalité)
The French Ministry for the Interior recognizes TEF Integration, Residence, and Nationality. Individuals must fulfill this condition to apply for a resident card or naturalization in France.
It assesses French oral and written comprehension and expression. However, it only measures language skills rather than understanding of France’s history, society, and culture.
You must achieve a minimum of A1 in all 4 sections to validate the citizen course. Also, A2 is for the resident card, and B1 is for the nationality application.
TEF IRN has four mandatory exams: written comprehension, oral comprehension, written expression, and oral expression.
All are computer-based group tests, except oral expression, which is face-to-face with an examiner. Completing the TEF IRN total test takes 1 hour and 15 minutes.
It measures your French competency up to B1 as per the CEFR. They send the results digitally within 2 to 4 weeks.
(iii) TEF Canada
The TEF Canada is a global exam that assesses general French proficiency. It is intended for both non-native French speakers and the Francophone population.
This test is mandatory for economic immigration programs to prove language skills. TEF for Canada immigration is essential for proving French language proficiency to get Canadian citizenship.
This test uses the same CEFR approaches as TEF Other Purposes. CIC needs this proof of French ability for permanent residence and citizenship applications. To earn bonus points, you need to be at least level 7 (CEFR B2).
The Canadian government also considers Provincial Nominee Programs (PNPs), self-employed workers, and start-up visa programs.
The test has four modules: listening, reading, speaking, and writing.
The e-TEF allows you to take the reading, listening, and writing modules on a computer at the specified test center. Infrastructure capacity limits the number of seats available for e-TEF.
To immigrate to Canada, you must complete all four sections mentioned above. The total duration is 2 hours and 55 minutes. Canadian citizenship applicants only need to go to the speaking and listening sections.
(iv) TEF Québec (TEFAQ)
Are you interested in immigrating to Québec through the Quebec Skilled Worker (QSW), Quebec Experience Program (PEQ), or other business programs?

In that situation, consider taking the Test d’évaluation du Français adapté pour le Québec (TEFAQ) to improve your total score.
It tests your speaking and listening capabilities. Quebec’s Ministry of Immigration, Diversity, and Inclusion (MIDI) includes the TEFAQ in its official immigration application.
The TEF Quebec has four parts. The primary focus is on verbal communication (speaking and listening), and the reading and writing sections are optional.
The test will last 2 hours and 55 minutes. To assess French, you must have a B2 level at the minimum. You will receive the results electronically.
By completing the oral comprehension and expression modules, you can gain a maximum of 14 points. You can increase your score by two points by completing the elective reading and writing papers.
The highest possible score is 16 points. Your spouse can earn up to six points if they also take the speaking and listening sections.
4. TCF (Test de Connaissance du Français)
Another French language placement test for non-native French speakers is the Test de Connaissance du Français (TCF).
The CIEP (Centre International d’études pédagogiques), an organization under the French Ministry of Education, oversees the TCF and has accredited it.

Like TEF, it has gained wide acceptance for jobs, academic admissions, and immigration.
Regardless of nationality or mother tongue, anyone aged 16 and above can take TCF Canada. The test confirms your French language skills for different objectives, such as immigration to France, Quebec, and Canada.
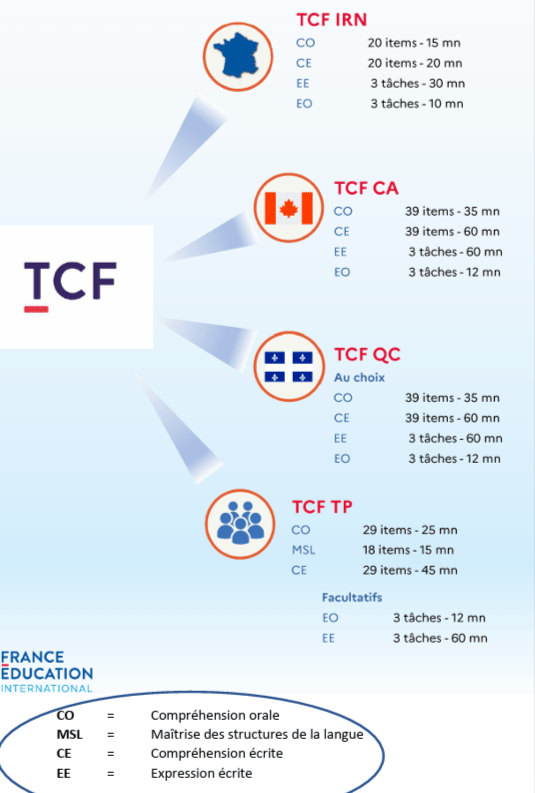
TCF has four versions to address diverse needs.
- TCF Tout Public (TP)
- TCF IRN (Intégration, Résidence et Nationalité)
- TCF Canada
- TCF Québec Immigration (TEFAQ)
Let’s explore the individual test.
(i) Le TCF tout public (TCF TP)
The TCF Tout Public (TP) applies to various individuals and contexts, serving general purposes. The certification is beneficial for personal, educational, and professional reasons.
It evaluates the French language competency of non-native speakers at different levels, from beginners to advanced learners.
Like other versions of the TCF, this one comprises four main sections: listening comprehension, speaking expression, writing expression, and reading comprehension.
This version has three mandatory tests consisting of multiple-choice questions (MCQs). Two additional tests are optional. The candidate decides whether to take them based on their needs.
The time the TCF Tout public takes depends on the number of tests. It can range from 1 hour and 25 minutes to 2 hours and 37 minutes.
(ii) TCF IRN (Integration, Residence and Nationality)
The TCF IRN targets foreign nationals 16 years old and above who want to validate their French proficiency.
If you plan to apply for French nationality and a long-term residence permit, it’s helpful. As part of the OFII citizenship process, it can validate the A1 level.
TCF IRN test format includes 4 mandatory reading, listening, written, and verbal skills. It evaluates general French language proficiency. The exam lasts for 75 minutes.
It only assesses linguistic skills and does not consider French history, culture, customs, and society.
(iii) TCF Canada
TCF Canada fulfills the criteria set by Immigration, Refugees, and Citizenship Canada (IRCC).
For economic immigration or gaining Canadian citizenship, they accept both TEF Canada and TCF Canada results.
The IRCC has accredited TCF Canada. Starting May 1, 2022, the Ministry of Inclusion, Francization, and Immigration (MIFI) will accept this as part of a Québec immigration application.
The format of the TCF Canada exam includes 78 items that test listening and reading comprehension. Each question is multiple-choice, and candidates must select one correct answer from 4 options.
Four mandatory sections are: listening, reading, writing, and speaking. The duration of the TCF Canada is 2 hours and 47 minutes.
(iv) TCF for Quebec
Quebec’s Ministry for Immigration, Diversity, and Inclusion (MIDI) approves the TCF for Quebec as a French proficiency test.
After achieving the score, you can add the certification to the application. This applies solely to your immigration application.
The “TCF for Quebec” comprises two mandatory (speaking and listening) and two optional exams. It estimates mastery in writing, reading, speaking, and listening in standard French.
The maximum points in these two components can give you a score of 14 out of 16 as a primary applicant.
5. Diplomas in French for Professions (DFP)

Diplômes de Français Professionnel (DFP) is another French language test meant for professional reasons. It certifies your ability to use oral and written French in professional contact.
DFP allows you to handle the company’s business’s interpersonal, administrative, and commercial aspects. Students or specialists who use French professionally can validate their knowledge with a diploma.
This diploma is targeted explicitly towards company staff or government personnel interacting with French-speaking contacts orally or in writing.
The minimum age is 16. A secondary-level education, computer savvy, and knowledge of how the professional world works are necessary.
It covers various activities and topics.
For example, form filing, writing notes and reports, talking to clients and decision-makers, describing your profession, and being aware of diverse business, social, and economic contexts and negotiations.
The Ministry of the Interior recognizes the Diplomas of Professional French for gauging French proficiency in a resident card or naturalization applications.
Business French offers five diplomas, from level A1 to C1, following CEFR. Unlike the TEF IRN, these diplomas are valid for life and boost your CV.
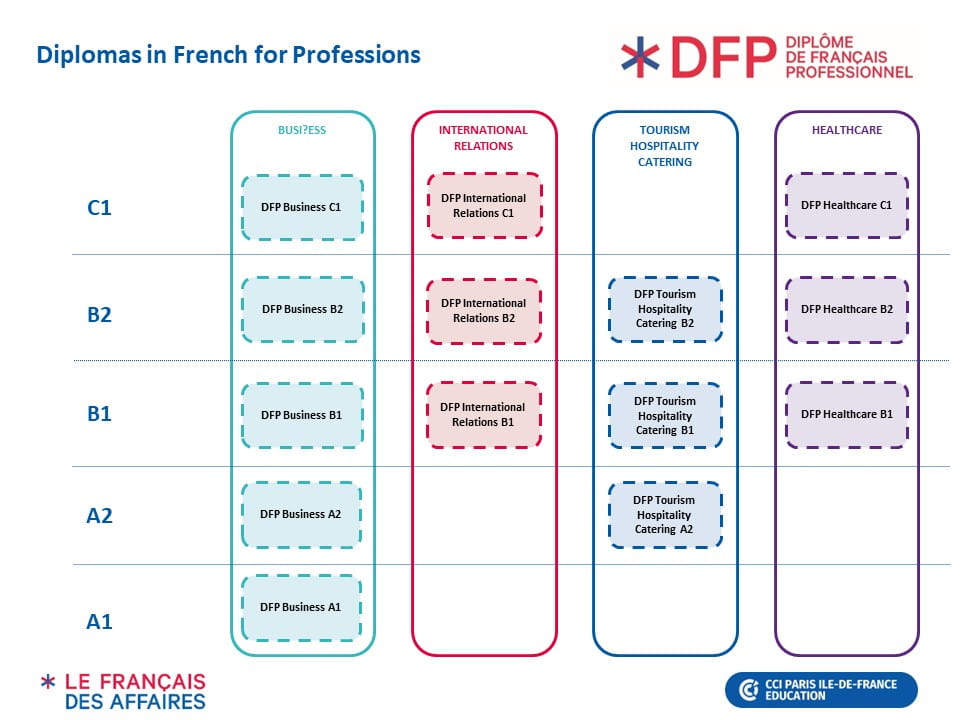
There are four different diplomas in French for professions.
(i) Diplôme de Français des Affaires (DFA)
If you want to enhance your chances of getting jobs related to French and get an international certification in Business French, you can take DFA.
DFP can improve your ability to work in local & international French-speaking societies and help develop new connections with French clients and colleagues. You can seek business prospects in a global environment.
To prepare for DFP Business, you must have a good grasp of business-related phrases, communication conventions, and language skills. You can expect tasks that simulate business scenarios, oral and written.
Many language schools and institutions offer preparatory courses for DFP exams. Business French offers five levels, from level A1 to C1.
(ii) Diplôme de Français des Relations Internatiional (DFRI)
A Diploma in French for International Relations (DFRI) is another exam that is part of DFP.
The Ministry of Europe and Foreign Affairs and the International Organization of La Francophonie requested the creation of a diploma in Professional French for International Relations.
The test checks comprehension and expression in international relations tasks. This is valid for life.
It meets the need for professional French training. The certification is for diplomats, international civil servants, and journalists who use French as their first or second working language.
This French exam covers several topics in this field, such as diplomacy, human rights, economics, peacemaking, finance, education, ecology, etc.
There are three Diplomas in French for International Relations, levels B1 to C1. There are no A1 and A2.
(iii) Pour Tourisme, de l’hôtellerie, et de la restauration
The Diploma in French for Tourism, Hospitality, and Catering assesses candidates’ written and oral communication levels. It evaluates their performance on reservations, client advising, and guided tours.
This diploma meets the need for professional French training and certification for non-native hospitality and travel industry speakers.
This diploma is for hotel, tourism, and food service professionals whose tasks include getting customers. Examples include receptionists, travel agents, tour operators, tour guides, event organizers, and headwaiters.
This test includes activities such as taking orders, welcoming clients, managing guest comments, preparing a guided tour plan, crafting promotional materials for a tourism offer, explaining a map, and offering advice to a client.
The Diploma in Tourism, Hospitality, and Catering has only three levels, from A2 to B2. Like other DFS exams, the scores are valid for a lifetime.
(iv) Diplôme de Français de la santé
The Diploma in French for Healthcare prepares you with French language skills for the medical and paramedical fields.
This diploma is perfect for medical professionals who want to improve their communication with patients, families, and healthcare specialists. Companies can also benefit from this diploma when expanding into the French-speaking market.
Many activities are part of the test. E.g., filling out medical forms, writing reports on medical risks, designing prevention tools, explaining a medical procedure, and discussing public health issues with non-specialists.
There are two levels: B1 and B2/C1. The B2/C1 level exam awards a diploma at either the B2 or C1 level, depending on the candidate’s performance.
6. TELC French
TELC, or the European Language Certificate, is a global test to assess language proficiency.
TELC provides language tests in 11 languages, including French, with over 80 certificates.
You can select the European language test section you prefer with this test.
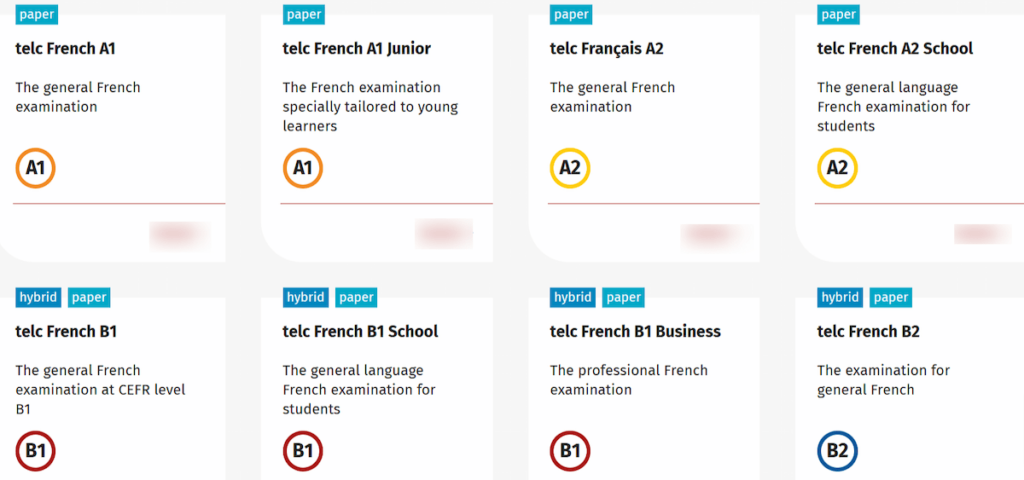
For instance, a general test for students, children, professionals, and custom-made content. French has four levels (A1, A2, B1, and B2).
Most tests contain a written and an oral part and follow CEFR levels. A1 and A2 are paper-based. On the other hand, B1 and B2 are hybrid, and you take in a computer or paper-based format.
- A1 — Anyone can take this test after 100-150 hours of French study.
- A1 Junior — Same as A1, but for children about 12 years old.
- A2 — Anyone can take this test after 200-250 hours of French study.
- A2 School — Same as A2 for children ages 12 to 16.
- B1 — This test is for those at the intermediate French level.
- B1 School — Same as A2, but for adolescents aged 14 to 17.
- B1 Business — Same as B1, but the test focuses more on various work situations.
- B2 — Anyone can take this exam that has achieved French proficiency at an advanced level.
Final Words on French Proficiency Exams

As with any language proficiency certification, take your time and choose the option that best suits you and aligns with your goals.
It’s advisable to check the specific requirements and preferences of institutions, employers, or academic programs. This is to ensure that the test meets your criteria.
Preparing for these exams typically involves focused language study, practice, and familiarity with the format.
Learning the language and taking the French proficiency test can open up a new world of opportunities and enrich your linguistic and cultural experiences.
You never know; it could be one of your best decisions ever and can make your French language journey worthwhile.
LanguageNext offers many French courses in Noida and online to suit individual needs. We also have tailor-made French classes for TEF and TCF Canada.
If you have questions, please ask them in the comment section below.